Abstract
Research Article
MRI-based Tumor Habitat Analysis for Treatment Evaluation of Radiotherapy on Esophageal Cancer
Shaolei Li, Shengguang Zhao, Yongming Dai, Yida He, Hongcheng Yang, Xuekun Zhang, Xiaoyan Chen, Weixiang Qi, Mei Chen, Yibin Zhang, Jiayi Chen, Fuhua Yan, Zenghui Cheng* and Yingli Yang*
Published: 24 June, 2024 | Volume 8 - Issue 1 | Pages: 055-063
Introduction: We aim to evaluate the performance of pre-treatment MRI-based habitat imaging to segment tumor micro-environment and its potential to identify patients with esophageal cancer who can achieve pathological complete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT).
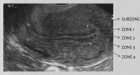
Material and methods: A total of 18 patients with locally advanced esophageal cancer (LAEC) were recruited into this retrospective study. All patients underwent MRI before nCRT and surgery using a 3.0 T scanner (Ingenia 3.0 CX, Philips Healthcare). A series of MR sequences including T2-weighted (T2), diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), and Contrast Enhance-T1 weighted (CE-T1) were performed. A clustering algorithm using a two-stage hierarchical approach groups MRI voxels into separate clusters based on their similarity. The t-test and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis were used to evaluate the predictive effect of pCR on habitat imaging results. Cross-validation of 18 folds is used to test the accuracy of predictions.
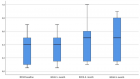
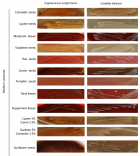
Results: A total of 9 habitats were identified based on structural and physiologic features. The predictive performance of habitat imaging based on these habitat volume fractions (VFs) was evaluated. Students’ t-tests identified 2 habitats as good classifiers for pCR and non-pCR patients. ROC analysis shows that the best classifier had the highest AUC (0.82) with an average prediction accuracy of 77.78%.
Conclusion: We demonstrate that MRI-based tumor habitat imaging has great potential for predicting treatment response in LAEC. Spatialized habitat imaging results can also be used to identify tumor non-responsive sub-regions for the design of focused boost treatment to potentially improve nCRT efficacy.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001065 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Habitat imaging; Esophageal cancer; MRI; Treatment evaluation
References
- Domper Arnal MJ, Ferrández Arenas Á, Lanas Arbeloa Á. Esophageal cancer: Risk factors, screening and endoscopic treatment in Western and Eastern countries. World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 14;21(26):7933-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.7933. PMID: 26185366; PMCID: PMC4499337.
- Nachiappan M, Kapoor VK. Esophageal Cancer: Whether and What Before or After Surgery? Indian J Surg Oncol. 2022 Dec;13(4):880-887. doi: 10.1007/s13193-022-01655-y. Epub 2022 Sep 26. PMID: 36687238; PMCID: PMC9845445.
- Hou H, Meng Z, Zhao X, Ding G, Sun M, Wang W, Wang Y. Survival of Esophageal Cancer in China: A Pooled Analysis on Hospital-Based Studies From 2000 to 2018. Front Oncol. 2019 Jun 27;9:548. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00548. PMID: 31316913; PMCID: PMC6610307.
- Brown LM, Devesa SS, Chow WH. Incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus among white Americans by sex, stage, and age. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008 Aug 20;100(16):1184-7. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djn211. Epub 2008 Aug 11. PMID: 18695138; PMCID: PMC2518165.
- Shibata A, Matsuda T, Ajiki W, Sobue T. Trend in incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus in Japan, 1993-2001. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2008 Jul;38(7):464-8. doi: 10.1093/jjco/hyn064. PMID: 18664481.
- Chien CR, Lin CY, Chen CY. Re: Incidence of adenocarcinoma of the esophagus among white Americans by sex, stage, and age. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009 Oct 21;101(20):1428; author reply 1429. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djp304. Epub 2009 Sep 1. PMID: 19724025.
- Kamangar F, Malekzadeh R, Dawsey SM, Saidi F. Esophageal cancer in Northeastern Iran: a review. Arch Iran Med. 2007 Jan;10(1):70-82. PMID: 17198458.
- Wu SX, Wang LH. Current status and perspectives of radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. Zhonghua Zhong liu za zhi [Chinese Journal of Oncology]. 2016; 38(9):650-654.
- Low DE, Kuppusamy MK, Alderson D, Cecconello I, Chang AC, Darling G, Davies A, D'Journo XB, Gisbertz SS, Griffin SM, Hardwick R, Hoelscher A, Hofstetter W, Jobe B, Kitagawa Y, Law S, Mariette C, Maynard N, Morse CR, Nafteux P, Pera M, Pramesh CS, Puig S, Reynolds JV, Schroeder W, Smithers M, Wijnhoven BPL. Benchmarking Complications Associated with Esophagectomy. Ann Surg. 2019 Feb;269(2):291-298. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002611. PMID: 29206677.
- D'Journo XB, Boulate D, Fourdrain A, Loundou A, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Gisbertz SS, O'Neill JR, Hoelscher A, Piessen G, van Lanschot J, Wijnhoven B, Jobe B, Davies A, Schneider PM, Pera M, Nilsson M, Nafteux P, Kitagawa Y, Morse CR, Hofstetter W, Molena D, So JB, Immanuel A, Parsons SL, Larsen MH, Dolan JP, Wood SG, Maynard N, Smithers M, Puig S, Law S, Wong I, Kennedy A, KangNing W, Reynolds JV, Pramesh CS, Ferguson M, Darling G, Schröder W, Bludau M, Underwood T, van Hillegersberg R, Chang A, Cecconello I, Ribeiro U Jr, de Manzoni G, Rosati R, Kuppusamy M, Thomas PA, Low DE; International Esodata Study Group. Risk Prediction Model of 90-Day Mortality After Esophagectomy for Cancer. JAMA Surg. 2021 Sep 1;156(9):836-845. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2021.2376. Erratum in: JAMA Surg. 2021 Sep 1;156(9):894. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2021.4340. PMID: 34160587; PMCID: PMC8223144.
- DeCesaris CM, Berger M, Choi JI, Carr SR, Burrows WM, Regine WF, Simone CB 2nd, Molitoris JK. Pathologic complete response (pCR) rates and outcomes after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy with proton or photon radiation for adenocarcinomas of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2020 Aug;11(4):663-673. doi: 10.21037/jgo-20-205. PMID: 32953150; PMCID: PMC7475327.
- Ge F, Huo Z, Cai X, Hu Q, Chen W, Lin G, Zhong R, You Z, Wang R, Lu Y, Wang R, Huang Q, Zhang H, Song A, Li C, Wen Y, Jiang Y, Liang H, He J, Liang W, Liu J. Evaluation of Clinical and Safety Outcomes of Neoadjuvant Immunotherapy Combined With Chemotherapy for Patients With Resectable Esophageal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Nov 1;5(11):e2239778. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.39778. PMID: 36322089; PMCID: PMC9631099.
- Parikh RR, Byun J, Goyal S, Kim IY. Local Therapy Improves Overall Survival in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Prostate. 2017 May;77(6):559-572. doi: 10.1002/pros.23294. Epub 2017 Jan 17. PMID: 28093791.
- Dagogo-Jack I, Shaw AT. Tumour heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018 Feb;15(2):81-94. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.166. Epub 2017 Nov 8. PMID: 29115304.
- Alfonso JCL, Berk L. Modeling the effect of intratumoral heterogeneity of radiosensitivity on tumor response over the course of fractionated radiation therapy. Radiat Oncol. 2019 May 30;14(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13014-019-1288-y. PMID: 31146751; PMCID: PMC6543639.
- Borggreve AS, Goense L, van Rossum PSN, Heethuis SE, van Hillegersberg R, Lagendijk JJW, Lam MGEH, van Lier ALHMW, Mook S, Ruurda JP, van Vulpen M, Voncken FEM, Aleman BMP, Bartels-Rutten A, Ma J, Fang P, Musall BC, Lin SH, Meijer GJ. Preoperative Prediction of Pathologic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Patients With Esophageal Cancer Using 18F-FDG PET/CT and DW-MRI: A Prospective Multicenter Study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2020 Apr 1;106(5):998-1009. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.12.038. Epub 2020 Jan 25. PMID: 31987972; PMCID: PMC7103753.
- Liu Z, Zhang XY, Shi YJ, Wang L, Zhu HT, Tang Z, Wang S, Li XT, Tian J, Sun YS. Radiomics Analysis for Evaluation of Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Dec 1;23(23):7253-7262. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1038. Epub 2017 Sep 22. PMID: 28939744.
- Shin J, Seo N, Baek SE, Son NH, Lim JS, Kim NK, Koom WS, Kim S. MRI Radiomics Model Predicts Pathologic Complete Response of Rectal Cancer Following Chemoradiotherapy. Radiology. 2022 May;303(2):351-358. doi: 10.1148/radiol.211986. Epub 2022 Feb 8. PMID: 35133200.
- Lu S, Wang C, Liu Y, Chu F, Jia Z, Zhang H, Wang Z, Lu Y, Wang S, Yang G, Qu J. The MRI radiomics signature can predict the pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 2024 Jan;34(1):485-494. doi: 10.1007/s00330-023-10040-4. Epub 2023 Aug 4. PMID: 37540319.
- Jardim-Perassi VB, Martinez G, Gillies R. Habitat imaging of tumor evolution by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). In: Radiomics and Radiogenomics: Technical Basis and Clinical Applications. 2019;115.
- Stringfield O, Arrington JA, Johnston SK, Rognin NG, Peeri NC, Balagurunathan Y, Jackson PR, Clark-Swanson KR, Swanson KR, Egan KM, Gatenby RA, Raghunand N. Multiparameter MRI Predictors of Long-Term Survival in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Tomography. 2019 Mar;5(1):135-144. doi: 10.18383/j.tom.2018.00052. PMID: 30854451; PMCID: PMC6403044.
- Lee DH, Park JE, Kim N, Park SY, Kim YH, Cho YH, Kim JH, Kim HS. Tumor Habitat Analysis Using Longitudinal Physiological MRI to Predict Tumor Recurrence After Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastasis. Korean J Radiol. 2023 Mar;24(3):235-246. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2022.0492. Epub 2023 Feb 6. PMID: 36788768; PMCID: PMC9971843.
- Park JE, Kim HS, Kim N, Park SY, Kim YH, Kim JH. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity in Multiparametric Physiologic MRI Is Associated with Patient Outcomes in IDH-Wildtype Glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Jan 1;27(1):237-245. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-2156. Epub 2020 Oct 7. PMID: 33028594.
- Lerttanatum N, Tharavej C, Chongpison Y, Sanpavat A. Comparison of tumor regression grading system in locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma after preoperative radio-chemotherapy to determine the most accurate system predicting prognosis. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2019 Apr;10(2):276-282. doi: 10.21037/jgo.2018.12.01. PMID: 31032095; PMCID: PMC6465493.
- Ajani JA, D'Amico TA, Bentrem DJ, Chao J, Corvera C, Das P, Denlinger CS, Enzinger PC, Fanta P, Farjah F, Gerdes H, Gibson M, Glasgow RE, Hayman JA, Hochwald S, Hofstetter WL, Ilson DH, Jaroszewski D, Johung KL, Keswani RN, Kleinberg LR, Leong S, Ly QP, Matkowskyj KA, McNamara M, Mulcahy MF, Paluri RK, Park H, Perry KA, Pimiento J, Poultsides GA, Roses R, Strong VE, Wiesner G, Willett CG, Wright CD, McMillian NR, Pluchino LA. Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Cancers, Version 2.2019, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2019 Jul 1;17(7):855-883. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2019.0033. PMID: 31319389.
- Martin-Romano P, Sola JJ, Diaz-Gonzalez JA, Chopitea A, Iragorri Y, Martínez-Regueira F, Ponz-Sarvise M, Arbea L, Subtil JC, Cano D, Ceniceros L, Legaspi J, Hernandez JL, Rodríguez J. Role of histological regression grade after two neoadjuvant approaches with or without radiotherapy in locally advanced gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2016 Sep 6;115(6):655-63. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.252. Epub 2016 Aug 18. PMID: 27537382; PMCID: PMC5023782.
- Piper J, Nelson A, Harper J. Deformable image registration in mim maestro evaluation and description. Cleveland, OH: MiM Software Inc,
- O'Connor JP, Rose CJ, Waterton JC, Carano RA, Parker GJ, Jackson A. Imaging intratumor heterogeneity: role in therapy response, resistance, and clinical outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Jan 15;21(2):249-57. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0990. Epub 2014 Nov 24. PMID: 25421725; PMCID: PMC4688961.
- Tomaszewski MR, Gillies RJ. The Biological Meaning of Radiomic Features. Radiology. 2021 Mar;298(3):505-516. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021202553. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Erratum in: Radiology. 2021 May;299(2):E256. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021219005. PMID: 33399513; PMCID: PMC7924519.
- Enderling H, Alfonso JCL, Moros E, Caudell JJ, Harrison LB. Integrating Mathematical Modeling into the Roadmap for Personalized Adaptive Radiation Therapy. Trends Cancer. 2019 Aug;5(8):467-474. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.06.006. Epub 2019 Jul 10. PMID: 31421904.
- Barzi A, Lenz HJ. Angiogenesis-related agents in esophageal cancer. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012 Oct;12(10):1335-45. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2012.707180. Epub 2012 Aug 4. PMID: 22860627.
- Liu Q, Zhang H, Jiang X, Qian C, Liu Z, Luo D. Factors involved in cancer metastasis: a better understanding to "seed and soil" hypothesis. Mol Cancer. 2017 Dec 2;16(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0742-4. PMID: 29197379; PMCID: PMC5712107.
- Bouleftour W, Rowinski E, Louati S, Sotton S, Wozny AS, Moreno-Acosta P, Mery B, Rodriguez-Lafrasse C, Magne N. A Review of the Role of Hypoxia in Radioresistance in Cancer Therapy. Med Sci Monit. 2021 Nov 3;27:e934116. doi: 10.12659/MSM.934116. PMID: 34728593; PMCID: PMC8573967.
- Cebulla J, Kim E, Rhie K, Zhang J, Pathak AP. Multiscale and multi-modality visualization of angiogenesis in a human breast cancer model. Angiogenesis. 2014 Jul;17(3):695-709. doi: 10.1007/s10456-014-9429-2. Epub 2014 Apr 10. PMID: 24719185; PMCID: PMC5538401.
- Hingerl L, Strasser B, Moser P, Hangel G, Motyka S, Heckova E, Gruber S, Trattnig S, Bogner W. Clinical High-Resolution 3D-MR Spectroscopic Imaging of the Human Brain at 7 T. Invest Radiol. 2020 Apr;55(4):239-248. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000626. PMID: 31855587.
- Zhang Y, Heo HY, Jiang S, Zhou J, Bottomley PA. Fast 3D chemical exchange saturation transfer imaging with variably-accelerated sensitivity encoding (vSENSE). Magn Reson Med. 2019 Dec;82(6):2046-2061. doi: 10.1002/mrm.27881. Epub 2019 Jul 1. PMID: 31264278.
- Brender JR, Saida Y, Devasahayam N, Krishna MC, Kishimoto S. Hypoxia Imaging As a Guide for Hypoxia-Modulated and Hypoxia-Activated Therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2022 Jan;36(1-3):144-159. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0176. PMID: 34428981; PMCID: PMC8856011.
Figures:
Similar Articles
-
Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging to differentiate benign and Malignant Parotid Gland TumorsSadia Ali,Adeena Khan*,Kiran Sarfaraz,Saba Akram,Mariam Javaid,Asma Bano. Diagnostic accuracy of Magnetic Resonance Imaging to differentiate benign and Malignant Parotid Gland Tumors. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001026; 2: 080-086
-
Percentage of Positive Biopsy Cores Predicts Presence of a Dominant Lesion on MRI in Patients with Intermediate Risk Prostate CancerJason M Slater,William W Millard,Samuel M Randolph,Thomas J Kelly,David A Bush*. Percentage of Positive Biopsy Cores Predicts Presence of a Dominant Lesion on MRI in Patients with Intermediate Risk Prostate Cancer. . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001025; 2: 073-079
-
Clinically and Radiological isolated syndrome (MS risk)Hassan Ahmed Hashem*,Yasser Hamed Mustafa,Abdelazim M Reda,Sameh Azab,Ahmed M Solaiman. Clinically and Radiological isolated syndrome (MS risk). . 2018 doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001020; 2: 041-046
-
Multiparametric MRI for the Assessment of Treatment Effect and Tumor Recurrence in Soft-tissue Sarcoma of the ExtremitiesRaul F Valenzuela*, Behrang Amini, Elvis Duran-Sierra, MA Canjirathinkal, John E Madewell, Colleen M Costelloe, William A Murphy. Multiparametric MRI for the Assessment of Treatment Effect and Tumor Recurrence in Soft-tissue Sarcoma of the Extremities. . 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001055; 7: 058-065
-
Contrast-enhanced Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (CE-SWI) for the Characterization of Musculoskeletal Oncologic Pathology: A Pictorial Essay on the Initial Five-year Experience at a Cancer InstitutionRaul F Valenzuela*, E Duran-Sierra, MA Canjirathinkal, B Amini, J Ma, KP Hwang, RJ Stafford, Keila E Torres, MA Zarzour, JA Livingston, JE Madewell, WA Murphy, CM Costelloe. Contrast-enhanced Susceptibility Weighted Imaging (CE-SWI) for the Characterization of Musculoskeletal Oncologic Pathology: A Pictorial Essay on the Initial Five-year Experience at a Cancer Institution. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001062; 8: 030-045
-
MRI-based Tumor Habitat Analysis for Treatment Evaluation of Radiotherapy on Esophageal CancerShaolei Li, Shengguang Zhao, Yongming Dai, Yida He, Hongcheng Yang, Xuekun Zhang, Xiaoyan Chen, Weixiang Qi, Mei Chen, Yibin Zhang, Jiayi Chen, Fuhua Yan, Zenghui Cheng*, Yingli Yang*. MRI-based Tumor Habitat Analysis for Treatment Evaluation of Radiotherapy on Esophageal Cancer. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001065; 8: 055-063
-
Radiomics by Quantitative Diffusion-weighted MRI for Predicting Response in Patients with Extremity Soft-tissue Undifferentiated Pleomorphic SarcomaRF Valenzuela*, E Duran-Sierra, M Canjirathinkal, B Amini, KE Torres, RS Benjamin, J Ma, WL Wang, KP Hwang, RJ Stafford, C Wu, AM Zarzour, AJ Bishop, S Lo, JE Madewell, R Kumar, WA Murphy Jr, CM Costelloe. Radiomics by Quantitative Diffusion-weighted MRI for Predicting Response in Patients with Extremity Soft-tissue Undifferentiated Pleomorphic Sarcoma. . 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001066; 8: 064-071
-
Microcystic Meningioma: Atypical Meningioma Revisited. Rare Case Report with Review of LiteratureKaustubh Gupta*. Microcystic Meningioma: Atypical Meningioma Revisited. Rare Case Report with Review of Literature. . 2025 doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001079; 9: 046-049
Recently Viewed
-
The Inverse Relationship between Acute Myocardial Infarction and Dissolved Oxygen Levels in WaterArturo Solís Herrera*,María del Carmen Arias Esparza,Ruth Isabel Solís Arias. The Inverse Relationship between Acute Myocardial Infarction and Dissolved Oxygen Levels in Water. J Nov Physiother Rehabil. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jnpr.1001066; 9: 013-023
-
The evolving landscape of ENT disorder treatments: Recent advances and innovations (2019-2021) – A CommentaryYRKM Sai*. The evolving landscape of ENT disorder treatments: Recent advances and innovations (2019-2021) – A Commentary. Adv Treat ENT Disord. 2021: doi: 10.29328/journal.ated.1001012; 5: 001-004
-
The role of islamic lifestyle and healthy nutrition in accordance with the recommendations of islam and the holly quran by focusing on the risk of cancer incidentRoya Dolatkhah*,Pooneh Jabbaripour,Mohammad Hossein Somi,Ali Roshani. The role of islamic lifestyle and healthy nutrition in accordance with the recommendations of islam and the holly quran by focusing on the risk of cancer incident. J Community Med Health Solut. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmhs.1001002; 1: 018-022
-
Myeloid Neoplasms: Better Understanding of their Molecular Pathogenesis with Improvised Genomic Testing: A Ray of Hope for Better Clinical OutcomesBhardwaj Tina Neelesh*, Phani MN. Myeloid Neoplasms: Better Understanding of their Molecular Pathogenesis with Improvised Genomic Testing: A Ray of Hope for Better Clinical Outcomes. J Hematol Clin Res. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.jhcr.1001027; 8: 001-007
-
Prevalence and Risk Factors to Preterm Labor through a Study in Jiblah University Hospital, Ibb, Governorate, YemenAfaf Alsharif*,Zainab Said,Fatima Mokabes,Leena Ameen,Alya Alqadri,Thekra Musaed,Bushra Musaed,Ala’a Ahmed,Halaa Rigih. Prevalence and Risk Factors to Preterm Labor through a Study in Jiblah University Hospital, Ibb, Governorate, Yemen. J Community Med Health Solut. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jcmhs.1001053; 6: 020-026
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."