Abstract
Research Article
HRCT imaging features of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease
Xiao Zhang*, Zexuan Zhou, Guangfeng Zhang, Ting Xu and Haobo Lin
Published: 27 April, 2021 | Volume 5 - Issue 1 | Pages: 035-041
Background: The aim of the study was to evaluate radiographic features of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease.
Patients and methods: 116 patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) from 2010 to 2019 comprised our retrospective study. All patients were subject to high resolution computed tomography (HRCT). ILD patterns were classified into 7 patterns as IIPs and analyzed with pathology. We chose two staging method and two semi-quantitative score methods to evaluate the HRCT performance and analyzed with pulmonary function tests.
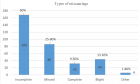
Results: Ground-glass opacities were the most common presentation on HRCT, followed by interlobular septal thickening, reticular opacities, intralobular interstitial thickening; honeycombing, traction bronchiectasis and nodules can also be observed. The most common pattern of SSc-ILD was nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), secondly was UIP. There was no difference in ILD pattern between HRCT and pathology, and revealed a high congruence. The four HRCT evaluating methods presented in this study all had significant relationships with PETs.
Conclusion: The most common pattern of SSc-ILD was nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP). The ILD patterns of HRCT coincide very well with histology, and will replace pathology as the gold standard for diagnosis and evaluation of SSc-ILD.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001036 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Systemic sclerosis; Interstitial lung disease; High resolution computed tomography
References
- Mouthon L, Berezné A, Brauner M, Kambouchner M, Guillevin L, et al. Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis. Presse Med. 2006; 35: 1943-1951.
- Masi AT. Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Arthritis Rheum. 1980; 23: 581-590. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7378088/
- Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, Johnson S, Sindhu R, et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American college of rheumatology/European league against rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72: 1747-1755. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24092682/
- Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, King TE, Lynch DA, et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement: Update of the International Multidisciplinary Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2013; 188: 733-748. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24032382/
- Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Medi. 2011; 183: 788-824. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21471066/
- Yamanaka Y , Baba T , Hagiwara E, Yanagawa N, Takemura T, et al. Radiological images of interstitial pneumonia in mixed connective tissue disease compared with scleroderma and polymyositis/dermatomyositis. Eur J Radiol. 2018; 107: 26-32. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30292269/
- Austin JH, Müller NL, Friedman PJ, Hansell DM, Naidich DP, et al. Glossary of terms for CT of the lungs: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee of the Fleischner Society. Radiology. 1996; 200: 327-331. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8685321/
- Qiu JG, Pan JP, Yu SB, Xing W, et al. Clinical Value of HRCT in Staging Lung Interstitial in Connective Tissue Disease. J Pract Radiol. 2008: 41--46.
- Goh NSL, Desai SR, Veeraraghavan S, Hansell DM, Copley SJ, et al. Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 35: 213-221.
- Kazerooni EA, Martinez FJ, Flint A, Jamadar DA, Toews G. Thin-section CT obtained at 10-mm increments versus limited three-level thin-section CT for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: correlation with pathologic scoring. Ajr Am J Roentgenol. 1997; 169: 977-983. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9308447/
- Goldin JG, Lynch DA , Strollo DC, Suh RD, Schraufnagel DE, et al. High-Resolution CT Scan Findings in Patients With Symptomatic Scleroderma-Related Interstitial Lung Disease. Chest. 2008, 134: 358-367. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18641099/
- Pellegrino R, Viegi G, Brusasco V, Carpo RO, Brgos F, et al. Interpretative strategies for lung function tests. Eur Respir J. 2005; 26: 948-968. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16264058/
- Khanna D, Mittoo S, Aggarwal R, Proudman S, Susanna M, et al. Connective Tissue Disease-associated Interstitial Lung Diseases (CTD-ILD) -- Report from OMERACT CTD-ILD Working Group. J Rheumatol. 2015; 42: 2168-2171.. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25729034/
- Steen VD, Medsger TA. Changes in causes of death in systemic sclerosis, 1972–2002. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007; 66: 940-944. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17329309/
- Simeon CP, Armadans L, Fonollosa V, Solans R, Selva A, et al. Mortality and prognostic factors in Spanish patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology(Oxford). 2003; 42: 71-75. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12509616/
- Sampaio-Barros PD, Bortoluzzo AB, Marangoni RG, Rocha LF, Del Rio APT, et al. Survival, Causes of Death, and Prognostic Factors in Systemic Sclerosis: Analysis of 947 Brazilian Patients. J Rheumatol. 2012; 39: 1971-1978. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22896025/
- Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, Airo P, Cozzi F, et al. Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010; 69: 1809-1815. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20551155/
- Travis WD, Hunninghake G, King TE, David A, Colby TV, et al. Idiopathic nonspecific interstitial pneumonia: report of an American Thoracic Society project. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 177: 1338-1347. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18388353/
- Johkoh T, Muller NL, Colby TV, Ichikado K, Taniguchi H, et al. Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia: Correlation between Thin-Section CT Findings and Pathologic Subgroups in 55 Patients. Radiology. 2002; 225: 199-204. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12355005/
- Raghu G, Remy-Jardin M, Myers JL, Richeldi L, Ryerson CJ, er al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2018; 198: e44-68. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30168753/
- Yamanaka Y, Baba T, Hagiwara E, Yanagawa N, Takemura T, et al. Radiological Images of Interstitial Pneumonia in Mixed Connective Tissue Disease Compared with Scleroderma and Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis. Eur J Radiol. 2018; 107: 26-32. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30292269/
- Das A, Kumar A, Arrossi AV, Ghosh S, Highland KB. Scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease: principles of management. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2019; 13: 357-367. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30686069/
- Moore OA, Goh N, Corte T, Rouse H, Hennessy O, et al. Extent of disease on high-resolution computed tomography lung is a predictor of decline and mortality in systemic sclerosis-related interstitial lung disease. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2013,52: 155-160. PubMed: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23065360/
Figures:
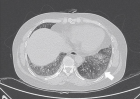
Figure 1
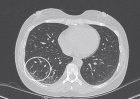
Figure 2
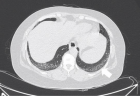
Figure 3
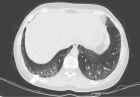
Figure 4
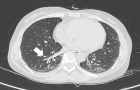
Figure 5
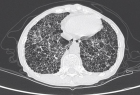
Figure 6
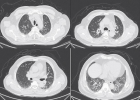
Figure 7
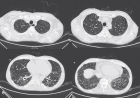
Figure 8
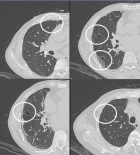
Figure 9
Similar Articles
-
HRCT imaging features of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung diseaseXiao Zhang*,Zexuan Zhou,Guangfeng Zhang,Ting Xu,Haobo Lin. HRCT imaging features of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. . 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001036; 5: 035-041
Recently Viewed
-
Chlorhexidine and oral cancer: A short reviewShrivardhan R Kalghatgi*,Mahesh R Khairnar,Tanushri Dalvi. Chlorhexidine and oral cancer: A short review. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001012; 4: 001-002
-
A retrospective study for Colorectal Cancer in Vlore, Albania-suggestions for further implicationsFatjona Kamberi*,Jerina Jaho. A retrospective study for Colorectal Cancer in Vlore, Albania-suggestions for further implications. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001013; 4: 003-006
-
Vegetables associated with reduced risk of cancerRobert Skopec*. Vegetables associated with reduced risk of cancer. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001014; 4: 007-014
-
Palliative care approach to oncological patient – Main pointsOnur Öztürk*,Muhammed Emin Göktepe,Mustafa Ünal. Palliative care approach to oncological patient – Main points. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001015; 4: 015-016
-
Minimally invasive gracilis muscle transposition: Initial reportTobias Machado*,Anis Taha. Minimally invasive gracilis muscle transposition: Initial report. Arch Cancer Sci Ther. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.acst.1001016; 4: 017-018
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."