Abstract
Mini Review
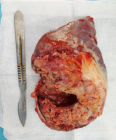
Which is the best? Palliative Radiation Therapy to Spleen or Splenectomy
Yasemin Benderli Cihan*
Published: 09 February, 2018 | Volume 2 - Issue 1 | Pages: 003-008
Spleen is one of the most important organ of the reticuloendothelial system and coordinates the immune response. Splenectomy is performed for hypersplenism, and staging of hematological malignancy. In conservatively followed patients, radiation therapy can be used to reduce hypersplenism symptoms. Splenectomy or palliative radiotherapy to spleen may probably cause an immune suppressive condition. This may probably local and systemic complications.
Read Full Article HTML DOI: 10.29328/journal.jro.1001015 Cite this Article Read Full Article PDF
Keywords:
Spleen, reticuloendothelial system, gastrointestinal malignancies, splenic irradiation
References
- Mogestern L. A history of splenectomy, in Hiatt JR, Philips EH, Morgenstern L (eds): sutgical Diseases of the S pleen. Berlin-Heidelberg-Verlag. 1997; 3.
- Mebius RE, Kraal G. Structure and function of the spleen. Nature Rev Immunol. 2005; 5: 606-616. Ref.: https://goo.gl/yz37Qi
- Bowdler AJ (editör). The Complete Spleen: Structure, Function, and clinical Disorders. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ (2nd edition). 2002; 140: 18-47.
- Rubin LG, Schaffner W. Clincial practice. Care of the asplenic patient. N Eng J Med. 2014; 371: 349-56. Ref.: https://goo.gl/wZ3UW2
- Altamura M, Caradonna L, Amati L, Pellegrino NM, Urgesi G, et al. Splenectomy and sepsis: the role of the spleen in the immune-mediated bacterial clearance. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2001; 23: 153-61. Ref.: https://goo.gl/p63YLC
- Cihan YB, Yokus O, Mutlu H. The role of palliative radiotherpy in symptomatic splenomegaly developing among elderly patients with chronic myleoproliferative disorders. Turkish Journal of Geriatrics. 2012; 15: 34-39.
- Wardemann H, Boehm T, Dear N, Carsetti R. B-1a B cells that link the innate and adaptive immune responses are lacking in the absence of the spleen. The Journal of Experimental Medicine. 2002; 195: 771. Ref.: https://goo.gl/8YzkKy
- Pozo AL, Godfrey EM, Bowles KM. Splenomegaly: investigation, diagnosis and management. Blood Rev. 2009; 23: 105-111. Ref.: https://goo.gl/a9u19a
- Di Sabatino A, Carsetti R, Corazza GR. Post-splenectomy and hyposplenic states. Lancet. 2011; 378: 86-97. Ref.: https://goo.gl/btiRav
- Ziemski JM, Rudowsi WJ. Evaluation of early postsplenektomy complications. Surg Gyne Obs. 1987; 165: 507-515.
- Rogers ZR, Wang WC, Luo Z, Iyer RV, Shalaby-Rana E, et al. Biomarkers of splenic function in infants with sickle cell anemia: baseline data from the BABY HUG Trial. Blood. 2011; 117: 2614-2617. Ref.: https://goo.gl/VVbd8v
- Bronte V, Pittet MJ. The spleen in local and systemic regulation of immunity. Immunity. 2013; 39: 806-818. Ref.: https://goo.gl/KakxSU
- Trip AK, Sikorska K, van Sandick JW, Heeg M, Cats A, et al. Radiation-induced dose-dependent changes of the spleen following postoperative chemoradiotherapy for gastric cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2015; 116: 239-244. Ref.: https://goo.gl/qUEaJs
- Schwartz PE, Sterioff S, Mucha P, Melton 3rd LJ, Offord KP. Postsplenectomy sepsis and mortality in adults. JAMA. 1982; 248: 2279-2283. Ref.: https://goo.gl/FQcqRv
- Wen SW, Everitt SJ, Bedő J, Chabrot M, Ball DL, et al. Spleen Volume Variation in Patients with Locally Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Receiving Platinum-Based Chemo-Radiotherapy. PLoS One. 2015; 10: 0142608. Ref.: https://goo.gl/9fwLuN
- Molrine DC, Siber GR, Samra Y, Shevy DS, MacDonald K, et al. Normal IgG and impaired IgM responses to polysaccharide vaccines in asplenic patients. Journal of Infectious Diseases. 1999; 179: 513-517. Ref.: https://goo.gl/CMAkWL
- Davies J, Barnes R, Milligan D. Update of guidelines for the prevention and treatment of infection in patients with an absent or dysfunctional spleen. Clinical Medicine. Clin Med (Lond). 2002; 2: 440-443. Ref.: https://goo.gl/azcNWK
- Newland A, Provan D, Myint S. Preventing severe infection after splenectomy: Patients should know the risks, be immunised, and take prophylactic antibiotics. BMJ: British Medical Journal. 2005; 331: 417. Ref.: https://goo.gl/nGp9au
- Styrt B. Infection associated with asplenia: risks, mechanisms, and prevention. Am J Med. 1990; 88: 33-42. Ref.: https://goo.gl/uPMqmV
- Appelbaum PC. Antimicrobial resistance in Streptococcus pneumoniae: an overview. Clin Infect Dis. 1992; 15: 77-83. Ref.: https://goo.gl/GcZTXc
- Kuranaga N, Kinoshita M, Kawabata T, Shinomiya N, Seki S. A defective Th1 response of the spleen in the initial phase may explain why splenectomy helps prevent a Listeria infection. Clinical & Experimental Immunology. 2005; 140: 11-21. Ref.: https://goo.gl/NuiLAq
- Maus UA, Waelsch K, Kuziel WA, Delbeck T, Mack M, et al. Monocytes are potent facilitators of alveolar neutrophil emigration during lung inflammation: role of the CCL2-CCR2 axis. J Immunol. 2003; 170: 3273-3278. Ref.: https://goo.gl/sE7DzW
- Barroso DE, Godoy D, Castiñeiras TMPP, Tulenko MM, Rebelo MC, et al. β-lactam Resistance, Serotype Distribution, and Genotypes of Meningitis causing Streptococcus pneumoniae, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. The Pediatric İnfectious Disease Journal. 2012; 31: 30. Ref.: https://goo.gl/zCsCzm
- Weinmann M, Becker G, Einsele H, Bamberg M. Clinical indications and biological mechanisms of splenic irradiation in chronic leukaemias and myeloproliferative disorders. Radiother Oncol. 2001; 58: 235-246. Ref.: https://goo.gl/HcErhi
- Paulino AC, Reddy SP. Splenic irradiation in the palliation of patients with lymphoproliferative and myeloproliferative disorders. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 1996; 13: 32-35. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ZPQxCK
- Bouabdallah R, Coso D, Gonzague-Casabianca L, et al. Safety and efficacy of splenic irradiation in the treatment of patients with idiopathic myelofibrosis: a report on 15 patients. Leukemia Research. 2000; 24: 491-495.
- Dailey MO, Coleman CN, Kaplan HS. Radiation-induced splenic atrophy in patients with Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1980; 302: 215-217. Ref.: https://goo.gl/bAaGAX
- Wagner H, McKeough PG, Desforges J, MadocJones H. Splenic irradiation in the treatment of patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia or myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia: results of daily and intermittent fractionation with and without concomitant hydroxyurea. Cancer. 1986; 58: 1207. Ref.: https://goo.gl/AnQACg
- Murray RG. The spleen. Histopathology of Irradiation (W. Bloom ed.) p.243. McGraw-Hill; New York. 1948.
- Spencer RP, Pearson HA. Splenic radiocolloid uptake in the presence of circulating Howell-Jolly bodies. J Nucl Med. 1973; 15: 294-295. Ref.: https://goo.gl/KgAAuT
- Looareesuwan S, Suntharasamai P, Webster HK, Ho M. Malaria in splenectomized patients: report of four cases and review. Clin Infect Dis. 1993; 16: 361-366. Ref.: https://goo.gl/yvGj24
- Coleman CN, McDougall IR, Dailey MO, Ager P, Bush S, et al. Stanford, California. Functional Hyposplenia After Splenic Irradiation for Hodgkin's Disease. Ann Intern Med. 1982; 96: 44-47. Ref.: https://goo.gl/NF1mKT
- Paulino AC, Reddy SP. Splenic irradiation in the palliation of patients with lymphoproliferative and myeloproliferative disorders. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 1996; 13: 32-35. Ref.: https://goo.gl/8ZmDyN
- Weinmann M, Becker G, Einsele H, Bamberg M. Clinical indications and biological mechanisms of splenic irradiation in chronic leukaemias and myeloproliferative disorders. Radiother Oncol. 2001; 58: 235-246. Ref.: https://goo.gl/TE3qcH
- de Porto AP, Lammers AJ, Bennink RJ, ten Berge IJ, Speelman P, et al. Assessment of splenic function. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2010; 29: 1465-1473. Ref.: https://goo.gl/Bz33J9
- McFarland JT, Kuzma C, Millard FE, Johnstone PA. Palliative irradiation of the spleen. Am J Clin Oncol. 2003; 26: 178-183. Ref.: https://goo.gl/zSni8u
- Elliott MA, Chen MG, Silverstein MN, Tefferi A. Splenic irradiation for symptomatic splenomegaly associated with myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. Br J Hematol. 1998; 103: 505. Ref.: https://goo.gl/eLZKGU
- Permentier C, Charbord P, Tibi M, Tubiana M. Splenic irradiation in myelofibrosis. Clinical findings and ferrokinetics. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1977; 2: 1075. Ref.: https://goo.gl/joAwxk
- Crary SE, Buchanan GR. Vascular complications after splenectomy for hematologic disorders. Blood. 2009; 114: 2861-2868. Ref.: https://goo.gl/HmEk5q
- Dailey MO, Coleman CN, Kaplan HS. Radiation-induced splenic atrophy in patients with Hodgkin’s disease and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1980; 302: 215-217. Ref.: https://goo.gl/mDTN8c
- Ugel S, Peranzoni E, Desantis G, Chioda M, Walter S, et al. Immune tolerance to tumor antigens occurs in a specialized environment of the spleen. Cell Rep. 2012; 2: 628-639. Ref.: https://goo.gl/frXK9Q
- Srisajjakul S, Prapaisilp P, Laorratkul N. Normal Splenic Volume Assessment on CT in 426 Adults. Siriraj Medical Journal. 2012; 64: 43-46.
- Gatenby PA, Mudan SS, Wotherspoon AC. Splenectomy for non-haematological metastatic malignant disease. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2011; 396: 625-638. Ref.: https://goo.gl/huWxaQ
- Weinmann M, Becker G, Einsele H, Bamberg M. Clinical Indications and Biological Mechanisms of Splenic Irradiation in Autoimmune Diseases. Strahlentherapie und Onkologie January. 2001; 177: 105-111. Ref.: https://goo.gl/ELU5n9
- Markus H, Forfar JC. Splenic irradiation in treating warm autoimmune hemolytic anaemia. Br Med J Clin Res Ed. 1986; 293: 839-840. Ref.: https://goo.gl/eHEgr7
Similar Articles
Recently Viewed
-
Forensic Insights into Multiple Stab Wounds: Autopsy Findings from a Case of Sixty Stab WoundsAsif Hussain*. Forensic Insights into Multiple Stab Wounds: Autopsy Findings from a Case of Sixty Stab Wounds. J Forensic Sci Res. 2025: doi: 10.29328/journal.jfsr.1001075; 9: 021-024
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024: doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
The relationship between IT consumption and anxiety in Pakistani youthWaqar Husain*,Sehrish Mobeen. The relationship between IT consumption and anxiety in Pakistani youth. Arch Psychiatr Ment Health. 2020: doi: 10.29328/journal.apmh.1001026; 4: 084-086
-
A Gecko-eye View of Naturalistic EnclosuresVictoria Davies, Abigail Heaman, James Brereton*. A Gecko-eye View of Naturalistic Enclosures. Insights Biol Med. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.ibm.1001026; 7: 013-019
-
Success, Survival and Prognostic Factors in Implant Prosthesis: Experimental StudyEpifania Ettore*, Pietrantonio Maria, Christian Nunziata, Ausiello Pietro. Success, Survival and Prognostic Factors in Implant Prosthesis: Experimental Study. J Oral Health Craniofac Sci. 2023: doi: 10.29328/journal.johcs.1001045; 8: 024-028
Most Viewed
-
Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth EnhancersH Pérez-Aguilar*, M Lacruz-Asaro, F Arán-Ais. Evaluation of Biostimulants Based on Recovered Protein Hydrolysates from Animal By-products as Plant Growth Enhancers. J Plant Sci Phytopathol. 2023 doi: 10.29328/journal.jpsp.1001104; 7: 042-047
-
Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case PresentationJulian A Purrinos*, Ramzi Younis. Sinonasal Myxoma Extending into the Orbit in a 4-Year Old: A Case Presentation. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001099; 8: 075-077
-
Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentialsDenis Tonini,Kai Wu,Renata Saha,Jian-Ping Wang*. Feasibility study of magnetic sensing for detecting single-neuron action potentials. Ann Biomed Sci Eng. 2022 doi: 10.29328/journal.abse.1001018; 6: 019-029
-
Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian TumorFaten Limaiem*, Khalil Saffar, Ahmed Halouani. Pediatric Dysgerminoma: Unveiling a Rare Ovarian Tumor. Arch Case Rep. 2024 doi: 10.29328/journal.acr.1001087; 8: 010-013
-
Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative reviewKhashayar Maroufi*. Physical activity can change the physiological and psychological circumstances during COVID-19 pandemic: A narrative review. J Sports Med Ther. 2021 doi: 10.29328/journal.jsmt.1001051; 6: 001-007

HSPI: We're glad you're here. Please click "create a new Query" if you are a new visitor to our website and need further information from us.
If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."